3D printing is a highly versatile manufacturing process that is capable of producing both prototypes and durable end-use parts. Certain applications require 3D printed parts to be extremely strong and durable. These characteristics depend, to a large extent, on the design as well as on the 3D printing materials used to manufacture the part. Let us take a look at the options of the strongest materials for 3D printing for the technologies available at Xometry.
Indicators of strong 3D printing materials
Strong materials or parts produced with them have high tensile, compact, or shear strength. They are able to withstand high stress and do not deform under heavy loads. Strong materials may also have good resistance to impact, chemicals, and harsh weather conditions. The strength of printed parts also depends on other factors, such as design, post-processing, and printing settings.

The strongest 3D printing materials available at Xometry
Different printing technologies require different plastics or metals to print. Let us see what print material with good strength each technology requires and its properties in detail.
Nylon PA 12 Carbon-filled
The blend of Nylon PA 12 resin with chopped carbon fibre gives this material excellent structural property. The carbon fibre occupies 35% of its weight. This allows for distinct freedom of design, especially for prototyping.
It is quite strong and rigid, capable of replacing metals in certain applications such as jigs, fixtures, drill guides and press-fit inserts. It has wide applications in the automobile, industrial and recreational industries. Nylon PA 12 CF is widely referred to as the FDM material with the highest strength to weight ratio available.
- 3D Printing technology: FDM
- Applications: Tooling, prototyping
Polycarbonate (PC)
Polycarbonate is a tough and amorphous material with high impact strength, stability and good electrical properties. This material allows the transmission of light internally in almost the same capacity as glass. It has a wider temperature range of usage with a heat deflection temperature of 140°C.
It is widely used for the production of safety helmets, lenses for car headlamps and bulletproof glasses. It can be combined with flame retardant materials without any significant material degradation.
- 3D Printing technology: FDM
- Applications: Medical equipment, industrial products, electronic components
Stainless Steel 17.4 / 1.4542
This is chromium-nickel copper steel with high strength and excellent toughness. It has a tensile strength of 1070N/mm2. Stainless Steel 17.4 has good corrosion resistance. Due to its high strength, it is heavily employed in the aerospace and high-technology driven industries in components such as gears, turbine blades, shafts, moulding dies.
This material can be heat treated to a wide variety of hardness and toughness levels. Direct metal laser sintering (DMLS) is the standard form of printing with stainless steel. However, other methods such as binder jetting and selective laser melting (SLM) are also used.
- 3D Printing technology: DMLS, binder jetting, SLM
- Applications: Aerospace, high-technology industries

ULTEM 1010
This material has the highest heat resistance, chemical resistance and tensile strength compared to other FDM thermoplastics. ULTEM 1010 is available in transparent, opaque and glass-filled grades. It has broad application in custom tools for metal or plastic parts fabrication, medical tools and temperature resistant dies.
It is a high-performance polyetherimide thermoplastic and can be said to be the strongest FDM printing material available. It has the lowest coefficient of thermal expansion. It has food-contact and biocompatibility certifications, which makes it ideal for applications in the food industry.
- 3D Printing technology: FDM
- Applications: Food industry, tooling

PEEK
It has excellent resistance to harsh chemicals with high mechanical strength and dimensional stability. It has the ability to retain its stiffness at elevated temperatures and can be employed for continuous use at temperatures up to 170°C.
PEEK, also known as Polyetheretherketone, has excellent fatigue and stress-crack resistance. It is used in aerospace, oil and gas and semiconductor production.
- 3D Printing technology: FDM
- Applications: Bearings, seals, valves, tubes
ULTEM 9085
This has a high strength–to–weight ratio, high impact strength with good heat resistance. It is highly flame retardant. It is used in the production of prototypes as well as tools in the aerospace and automotive industries. It is comparable to nylon 6.68 (9800).
ULTEM 9085 with its superior mechanical strength and lightweight is suitable for the production of end-use components.
- 3D Printing technology: FDM
- Applications: Jigs, fixtures, composite moulds
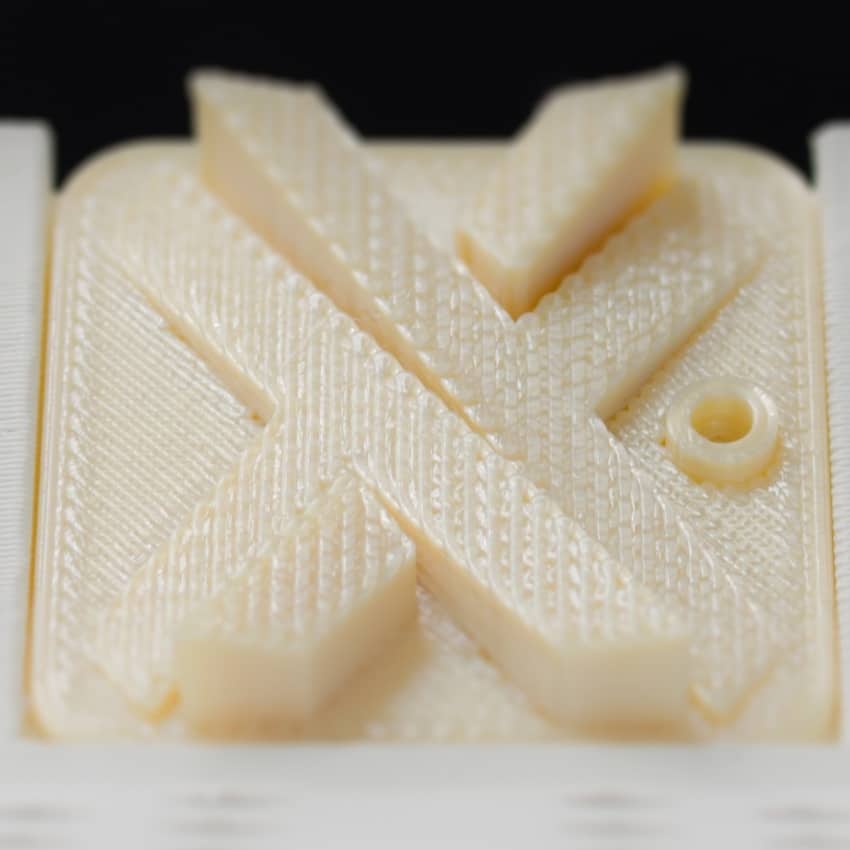

Aluminum AlSiMG / EN 1706: 1998
This material has excellent strength at elevated temperatures (about 200°C). Aluminum AlSiMG has good corrosion resistance and can be easily polished. It has good workability and good heat crack resistance. The fatigue strength is excellent at 110N/mm2.
It has good weldability and is widely applied in parts for vehicles, machines and aircraft. It has a tensile strength of 290MPa at room temperature.
- 3D Printing technology: DMLS
- Applications: Automotive, aerospace
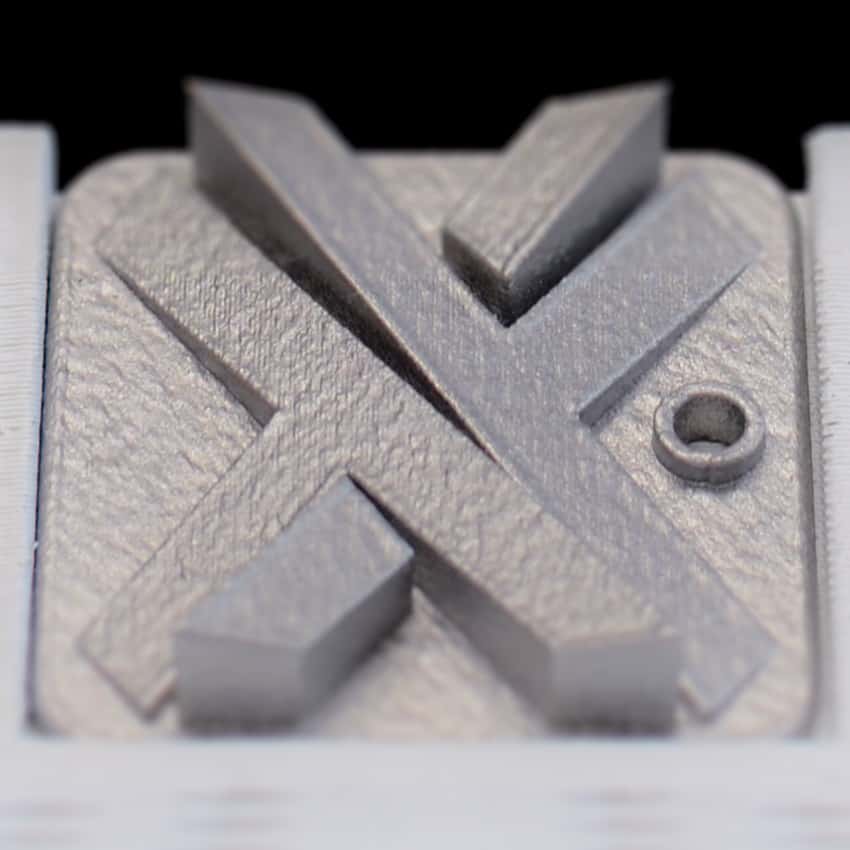

Stainless Steel 316L / 1.4404
This material has low carbon content and is chromium-nickel-molybdenum stainless steel. Stainless Steel 316L has excellent corrosion resistance and stability against chlorine-based media and non-oxidizing acids. It has a high tensile strength of about 500N/mm2.
It is typically used in food processing and laboratory equipment, heat exchangers, nuts and bolts. It is the smoothest material when compared with other metal materials.
- 3D Printing technology: DMLS
- Applications: Food and beverage equipment, pharmaceutical equipment

3D printing strongest materials comparison
Let’s have a comparison of the three resins from Xometry’s quoting engine for the CAD model:
| Material | Technology | Tensile Strength |
| Nylon PA 12 CF | FDM | 76 MPa |
| PC | FDM | 60 MPa |
| Stainless Steel 17.4 | DMLS | 1103 MPa |
| ULTEM 1010 | FDM | 105 MPa |
| PEEK | FDM | 110 Mpa |
| ULTEM 9085 | FDM | 70 MPa |
| Aluminum AlSiMG | DMLS | 230 - 290 MPa |
| Stainless Steel 316L | DMLS | 490 - 690 MPa |
Try out Xometry's Instant Quoting Engine to source your parts with the strongest 3D printing materials.
Conclusion
There are two main types of strong materials for 3D printing: plastics, which can be printed with FDM, SLS, SLA, SLM, MJF. Xometry Asia offers fast, reliable, and highly accurate 3D printing services with these technologies and materials. Through our Instant Quoting Engine and our network of over 10,000 manufactures, we ensure that you experience a seamless part production process, from quoting to doorstep delivery.